1.What is 1020 mild steel plate?
1020 steel sheet refers to a low-carbon steel sheet (also called mild steel plate) made of 1020 steel. The steel sheet is a flat metal plate made by pouring molten steel and pressing it after cooling. According to the material, steel sheet includes mild steel plate, low-alloy high-strength steel plate, stainless steel plate, etc.AISI 1020 Steel is a mild steel, where "1020" means that the carbon content of this steel is about 0.20%. It is normally used in turned and polished or a cold drawn condition. AISI is the abbreviation of "American Iron and Steel Institute". This is a trade association representing the American steel industry, which is responsible for formulating and publishing standards and specifications for steel products.

We sometimes see the expression SAE 1020 steel, which is actually the same material as AISI 1020, but with different naming standards. SAE is the acronym for "Society of Automotive Engineers".
(1) Chemical Composition

(2) Physical Properties

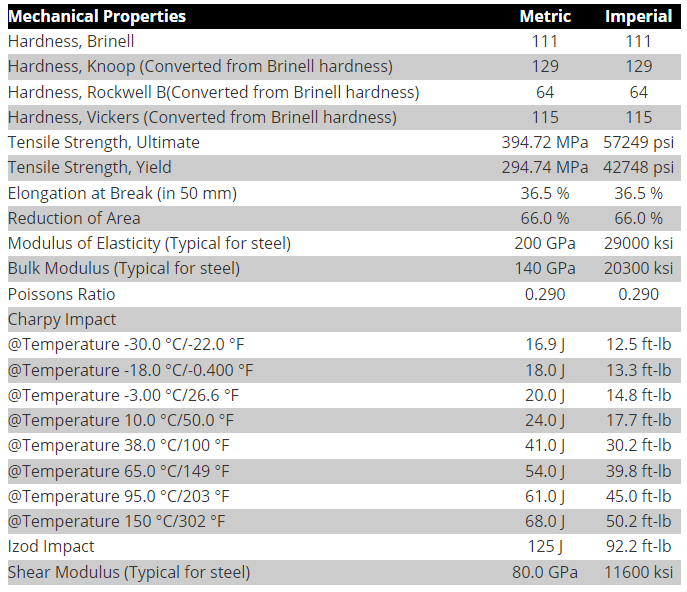
(3) Mechanical Properties
2.What is 1020 steel plate good for?
The annealed structure of low carbon steel is ferrite and a small amount of pearlite. Its strength and hardness are low, but its plasticity and toughness are good. Therefore, its cold formability is good, and it can be cold formed by curling, bending, stamping and other methods. This 1020 steel also has good weldability and plasticity, which is conducive to cutting, welding and processing.Characteristics of 1020 steel plate:
①Good toughness and plasticity
The annealed structure of low carbon steel is ferrite and a small amount of pearlite, with low strength and hardness, but good plasticity and toughness. Therefore, 1020 steel plate has good cold formability and can be cold formed by curling, bending, stamping and other methods.
②Easy to weld
The low carbon content makes the steel easy to fuse during welding, and the mechanical properties of the welded joint are good.
③Effective surface hardening cannot be achieved
Due to the low carbon content of 1020 steel, the hardened structures such as martensite or bainite formed during induction heating or flame heating are less, resulting in its hardening effect not being as obvious as that of high carbon steel.
3.Application of 1020 metal steel plate
Common uses of 1020: shim plates, gusset plates, bridge plates, bearing plates, robot bases, column base plates, press parallels, press platens, tooling plates, machine plates, machine frames and pedestals, steel table tops, base plates, mold & die, machine mounting plates, etc.
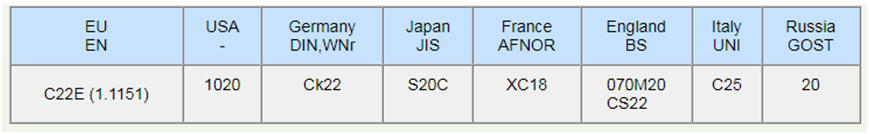
4.What is a 1020 steel grade equivalent to?