1.What is conductor casing?
OCTG casing can be divided into four types according to different usage methods: surface casing, intermediate casing, conductor casing and production casing. The first layer of casing run into the well structure is called theconductor casing. Its function is to maintain the surface layer near the wellhead.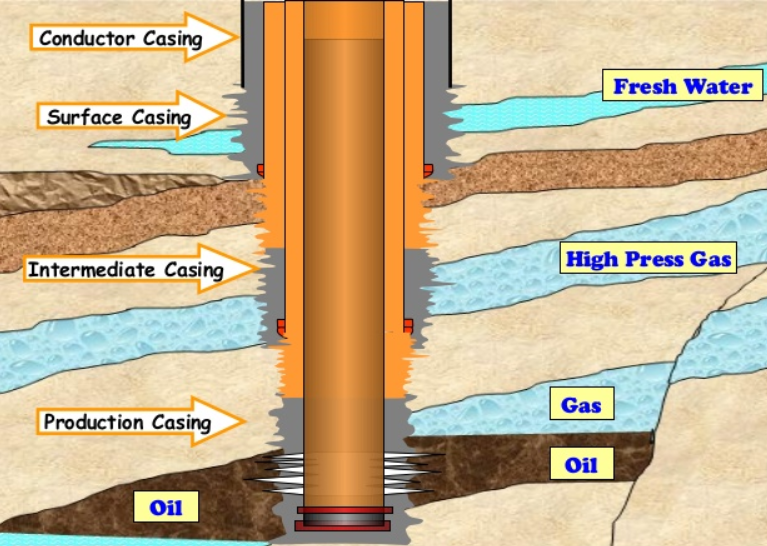
2.Conductor casing vs surface casing
Conductor casing and surface casing serve distinct roles in the construction of a well. The conductor casing is the first casing string installed and is typically shorter compared to the surface casing. Its primary function is to provide structural integrity and prevent the collapse of the wellbore during initial drilling operations, particularly in loose and unconsolidated surface formations. Additionally, it serves to protect shallow sands from contamination by drilling fluids and helps prevent washouts near the surface.On the other hand, surface casing is a deeper casing string that is installed after the conductor casing. It extends further into the well and is designed to isolate and protect groundwater aquifers from potential contamination by drilling fluids and formation fluids. Surface casing also provides a stable foundation for subsequent casing strings and wellbore equipment. Its placement is governed by regulatory requirements to ensure environmental and safety standards are met during drilling operations.
3. Physical dimensions of the conductor casing
Conductor casing sizes, depth, and length play vital roles in the construction and integrity of a wellbore.The size of conductor casing is determined by various factors, including the diameter of the wellbore and the anticipated downhole conditions. Common sizes range from a few inches to over a foot in diameter.
The depth of conductor casing refers to the vertical extent to which the casing is installed into the earth. This depth is typically shallow, penetrating only the uppermost formations to provide structural support and prevent well collapse during initial drilling operations.
The length of conductor casing, on the other hand, varies depending on the specific geological characteristics of the drilling site and the requirements of the well design. It is often shorter compared to subsequent casing strings and is primarily designed to protect shallow formations from contamination and provide stability near the surface.
4.How to set conductor casing?
Setting conductor casing involves several steps:(1)Preparation
Before setting the conductor casing, the well site must be prepared, which includes clearing the area and excavating a starter hole.(2)Installation
The conductor casing is typically lowered into the starter hole using a casing running tool or casing elevator attached to the drilling rig. The casing is gradually lowered into the hole until it reaches the desired depth.(3)Placement
Once the conductor casing reaches the desired depth, it is firmly set into place by pumping cement or drilling mud through the casing string. This process, known as cementing or mud displacement, helps secure the casing in the wellbore and creates a barrier between the casing and the surrounding formations.(4)Verification
After the cementing process is complete, the depth and integrity of the conductor casing are verified using downhole tools or logging techniques to ensure that it is properly set and sealed.(5)Completion
Once the conductor casing is successfully set and verified, drilling operations can proceed to the next phase, which may involve drilling deeper into the wellbore and installing additional casing strings as needed.
Previous:Surface casing
Next:Casing string









